4.1.2. Potential Interprocess Communication Problems¶
Interprocess communication (IPC) requires the use of resources, such as memory, which are shared between processes or threads. If special care is not taken to correctly coordinate or synchronize access to shared resources, a number of problems can potentially arise.
4.1.2.1. Starvation¶
A starvation condition can occur when multiple processes or threads compete for access to a shared resource. One process may monopolize the resource while others are denied access.
4.1.2.2. Deadlock¶
A deadlock condition can occur when two processes need multiple shared resources at the same time in order to continue.

These two pirates are in deadlock because neither is willing to give-up what the other pirate needs.¶
A Computer Example of Deadlock:
Thread A is waiting to receive data from thread B. Thread B is waiting to receive data from thread A. The two threads are in deadlock because they are both waiting for the other and not continuing to execute.
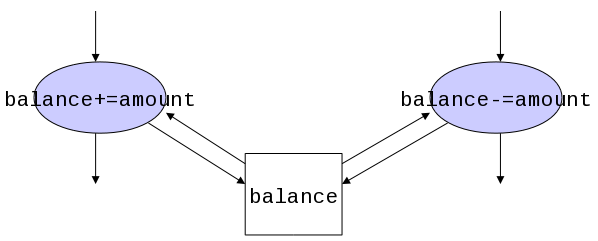
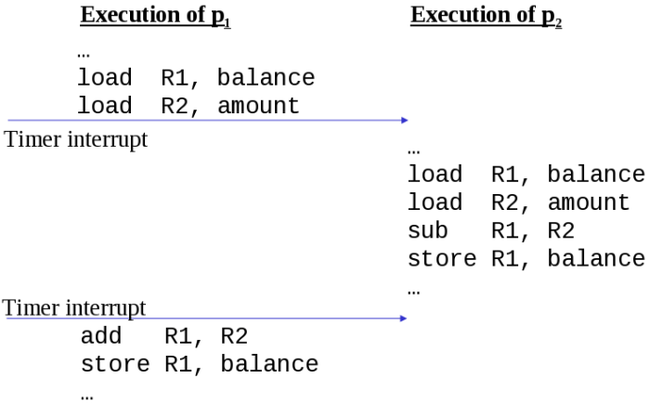
4.1.2.3. Data Inconsistency¶
When shared resources are modified at the same time by multiple resources, data errors or inconsistencies may occur. Sections of a program that might cause these problems are called critical sections. Failure to coordinate access to a critical section is called a race condition because success or failure depends on the ability of one process to exit the critical section before another process enters the critical section. It is often the case that two processes are seldom in the critical section at the same time; but when there is overlap in accessing the critical section, the result is a disaster.